
Where in the World?
Understanding Latitude and Longitude

Where in the World?
Understanding Latitude and Longitude
A Learning
Module
developed by Mrs. Cirino
for our 4th Grade Classroom
The purpose of this learning module is for you to learn how to use longitude and latitude to locate various cities, regions, landforms, and bodies of water around the globe. We will use The New York Times Learning Network’s crossword puzzle “Longitude and Latitude” to sharpen our atlas skills.
![]() Think
Sheet #1
Think
Sheet #1
Let's begin our module by exploring our atlases. In your teams, look through an atlas and note down answers to the following questions:
§ What different types of maps are found in the atlas?
§ What other information on countries and locations is provided in the atlas?
§ What tools does the atlas provide so that you can quickly find a location?
Be prepared to share your answers with the rest of the class.
![]() Think
Sheet #2
Think
Sheet #2
Read the New York Times article, “Latitude and Longitude Tutorial” in your team and discuss it.
Use your atlases to answer the questions on the worksheet. Work as a team and compare your answers. Talk about the different ways you can find the answers to the questions.
![]() Think
Sheet #3
Think
Sheet #3
Now, we are ready to complete the The New York Times Learning Network’s “Latitude and Longitude” crossword puzzle. Thirty of the puzzle clues will ask you to use an atlas to find a location. The clues that require an atlas are:
“Across” Clues: 1, 9, 13, 14, 16, 18, 23, 32, 33, 44, 47, 49, 51, 59, 62, 67
“Down” Clues: 2, 5, 10, 15, 17, 24, 28, 29, 43, 51, 53, 55, 56, 61
Work together to find answers to all of the clues on the crossword puzzle. You can also use the references in the tutorial to find your answers. Good luck!
Our Final Activities:
Okay, we are now ready to create our own crossword puzzles. Working in your groups, make a crossword puzzle that contains clues for the words: North and South Poles, equator, prime meridian, the tropics, and hemispheres. Please use the vocabulary definitions listed on this page to help you.
The next activity will be to create a map of California that identifies the following characteristics:
§ The state capital
§ Descriptions of the various regions of California, including how their characteristics and physical environments (e.g., water, landforms, vegetation, climate) affect human activity.
§ Descriptions of how communities in California vary in land use, vegetation, wildlife, climate, population density, architecture, services, and transportation.
Be creative with this activity. I am going to keep the guidelines pretty open, because I really want to see how you come up with answers to the descriptions listed above by just working and thinking about it in your groups. As always, I'll be there to help, but think about the descriptions and use the Internet to research the regions and communities.
CONGRATULATIONS!
We just completed our first
Social Studies Learning Module!
Great Job!
 For
any students at home with far too much time on your hands:
For
any students at home with far too much time on your hands:
Challenge Activities:
§ What different types of maps have you seen?
§ What different types of maps can be found in an atlas and what are their purposes?
§ How do world maps, globes and atlases serve different purposes?
§ Why might latitude and longitude have been developed?
§ What types of people do you think use latitude and longitude in their daily lives and why?
§ What is the relationship of latitude and longitude to the study of geography?
§ Why are understanding how to use atlases and how to use latitude and longitude measurements important skills?
1. longitude:
§
longitude,
angular distance on the earth's surface measured along any latitude line such
as the equator east or west of the prime meridian. A meridian of longitude
is an imaginary line on the earth's surface from pole to pole; two opposite
meridians form a great circle dividing the earth into two hemispheres. By international
agreement, the meridian passing through the original site of the Royal Greenwich
Observatory at Greenwich, England, is designated the prime meridian, and
all points along it are at 0 longitude. All other points
on the earth have longitudes ranging from 0 to 180 E or from 0 to 180 W. Except
where it is changed to account for populated areas, the international date
line lies along the 180 meridian. Meridians of longitude
and parallels of latitude together form a grid by which any position
on the earth's surface can be specified. The term longitude
is also used in various celestial coordinate systems (see ecliptic coordinate
system).
© 2002 Columbia University Press (Information retrieved from BigChalk.com)
2. latitude:
World Book Encyclopedia (2002) 01-01-2002
LAT uh tood Latitude,
describes the position of a point on the earth's surface in relation to the equator. Latitude is one of the two grid coordinates that can be used to locate any point on the earth. The other coordinate is longitude.
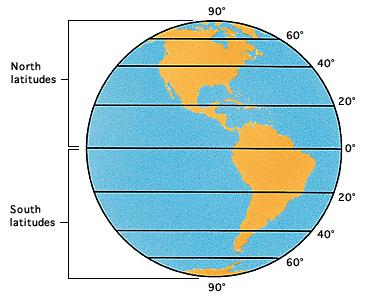
Latitude
Imagine a series of lines running around the earth parallel to the equator,
shown here. These are lines of latitude. Every point
on the earth's surface lies on such a line. It shows the position of that spot
in relation to the equator.
World Book Encyclopedia illustration by Sarah Woodward
The latitude of a point is measured in terms of its distance from the equator toward one of the earth's poles. Latitude is measured in degrees. Any point on the equator has a latitude of zero degrees (written 0 ). The North Pole has a latitude of 90 north and the South Pole has a latitude of 90 south. These two points are sometimes written +90 and -90 . Degrees of latitude are divided into 60 minutes ('), and the minutes each consist of 60 seconds (").
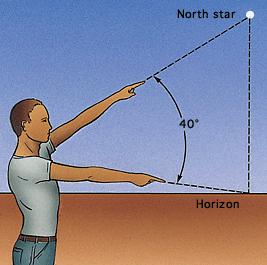
How to estimate latitude
A way to estimate latitude is to point one arm at the
North Star and the other at the horizon. The number of degrees of the angle
between your arms is about the latitude where you are.
World Book Encyclopedia illustration by Sarah Woodward
All points on the earth's surface that have the same latitude lie on an imaginary circle called a parallel of latitude. The distance between two parallels that are 1 apart is about 60 nautical (sea or air) miles, or 69 statute (land) miles or 111 kilometers. This length of 1 of latitude varies from 59.7 nautical miles near the equator to 60.3 nautical miles near the poles. The variation results because the earth is not a perfect sphere. A difference in latitude of 1 minute equals about 1 nautical mile.
See also Climate - The role of latitude; Equator; Longitude; Map.
© 2002 World Book, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. "World
Book" and the globe device are trademarks of World Book, Inc.
3. atlas:
Atlas
is usually a book of maps. It often includes facts and figures about places. The term atlas may also be used for volumes that present a subject in an illustrated or tabular form. A geographical atlas usually contains maps, charts, and tables. Maps may show cities, towns, roads, countries, rivers, mountains, the size and relationships of land and water areas, and the names of features and places. An index lists the names of such features and tells where to find them on the maps. Maps may also show the distribution of economic resources, population, types of climate, and plant life.
Standard atlases in the United States include Hammond's New World Atlas, Goode's World Atlas, and the Rand McNally Cosmopolitan World Atlas. The Rand McNally Commercial Atlas and Marketing Guide includes sales distribution maps, postal information, lists of national parks and monuments, and other valuable facts. Examples of large world atlases with relatively detailed maps are the Times Atlas of the World, the Touring Club Italiano Atlas, in Italian, and the Russian Atlas Mira. Several countries publish national atlases with maps showing physical, economic, and cultural resources. For example, the National Atlas of the United States is published by the U.S. Geological Survey.
In the A.D. 100's, Ptolemy, a geographer who lived in Egypt, published what most historians consider the first atlas. This was part of his Geography, an eight-volume work on mapmaking. Gerardus Mercator, a Flemish cartographer, first used the name atlas for a collection of maps in the late 1500's. Mercator may have used this name because an earlier collection of maps had on its title page an illustration of the Greek god Atlas supporting the earth on his shoulders.
Early cartographers drew the maps in their atlases by hand. The production of atlases increased with the invention of printing. Notable among the early atlases is Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570 by Abraham Ortelius of Antwerp.
See also Map.
© 2002 World Book, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. "World
Book" and the globe device are trademarks of World Book, Inc.
4. equator:
Equator
is the great circle of the earth that lies halfway between the North and South poles. This imaginary line divides the earth into two equal parts called the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the starting point for the degrees of latitude that measure distances north and south from the equator to the poles (see Latitude; ). The latitude of the equator is zero. On a globe, the equator is also a line on which equal distances are marked to show degrees of longitude, which measures east and west distances (see Longitude; ). The circumference of the earth at the equator is 24,901.55 miles (40,075.16 kilometers). Each degree of longitude at the equator equals 69.17 miles (111.32 kilometers).
The location of the equator can be determined by observing the elevation of the North Star or the sun above the horizon. Allowing for slight corrections, the angle of elevation of the North Star at any given place equals the latitude of that place. Thus, at the equator, the North Star is barely visible above the horizon and has an elevation of nearly zero degrees.
The equatorial climate.
The climate along the equator varies according to altitude and the distance from the sea. In most equatorial lowlands, heavy rains and average temperatures are uniform all year. But the east coast of Africa has only light rain and a long dry season. Quito, Ecuador, which lies almost exactly on the equator, has an elevation of 9,350 feet (2,850 meters). It has a uniform temperature that is about 25 Fahrenheit degrees (14 Celsius degrees) cooler than nearby lowlands.
The celestial equator
is an imaginary circle that goes around the sphere in which the earth and heavenly bodies lie. It helps locate stars and planets. See Astronomy - Locating objects in space; .
The magnetic equator
is the line on which all points are equally distant from the north and south magnetic poles. See Magnetic equator.
© 2002 World Book, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. "World
Book" and the globe device are trademarks of World Book, Inc.
5. prime meridian:
§
prime meridian prime meridia,
meridian that is designated
zero degree (0 ) longitude, from which all other longitudes are measured. By
international convention, it passes through the original site of the Royal Observatory
in Greenwich, England; for this reason, it is sometimes called the Greenwich
meridian. Universal time, the standard
basis for determining time throughout the world, is civil time measured
at the prime meridian.
© 2002 Columbia University Press
Look on almost any map or globe and you will see lines going vertically and
horizontally, forming what looks like a grid over the Earth's surface. These
lines, called latitude and longitude, assign numbers to every location on the
map. The unit of measurement for latitude and longitude is called a degree,
which is indicated by a small circle to the upper left after a latitude or longitude
is given (ex. 60°).
Latitude, the lines that run left to right on a map or globe, is always listed first when assigning a measurement. The equator is found at 0° latitude, and there are 90 degrees to each of the poles. The N or S following a latitude measurement indicate whether the degrees are measured north or south of the equator.
Longitude, the lines that run up and down on a map or globe, is always listed second when assigning a measurement. The prime meridian is found at 0° longitude, and there are 180° going both east and west from the prime meridian to the International Date Line. The E or the W following a longitude measurement indicate whether the degrees are measured east or west of the prime meridian.
Minutes and seconds sometimes follow latitude and longitude measurements to more accurately pinpoint a location. Each degree can be divided into sixty minutes, usually indicated by a single quotation mark (ex. 5') or by numbers following a period in the latitude or longitude measurement. For example, 90°15'N could also be written as 90.15N. Each minute can be divided into sixty seconds, indicated by a regular (double) quotation mark (ex. 5'').
You can use a map or globe to find general latitude and longitude measurements, or an atlas, which is a collection of maps, for more specific measurements including minutes and seconds. Practice using an atlas to find the following locations (be sure to include degree signs and direction):
What can be found at 90° N? ____________________
What can be found at 90° S? ____________________
What city in England is located at longitude 0°?____________________
What city in the United States is located at 40° N, 75° W? ____________________
What other cities are located at latitude 40° N? ____________________
What other cities are located at longitude 75° W? ____________________
Find your city on a map or atlas. At what latitude and longitude are you right now? ____________________
Find your country on a map or atlas. What is the approximate range of latitudes and longitudes that your country covers? ____________________
There are many online atlases and geography resources available if you don't have an atlas. Visit some of these sites, and see what they have to offer:
Earth Viewer (http://www.fourmilab.ch/earthview/vlatlon.html) allows you to view either a map of the Earth showing the day and night regions at this moment, or to view the Earth from the Sun; the Moon; the night side of the Earth; above any location on the planet specified by latitude, longitude and altitude; from a satellite in Earth orbit; or above various cities around the globe. The site is produced by Fourmilab of Switzerland.
Map Machine Atlas (http://www.nationalgeographic.com/resources/ngo/maps/) includes political and physical maps, flags, facts, and country profiles; from National Geographic.
Atlapedia Online (http://www.atlapedia.com/) contains full color physical and political maps as well as key facts and statistics on countries of the world.
![]() Return to Mrs. Cirino's Classroom Homepage
Return to Mrs. Cirino's Classroom Homepage